1. Electrical Topology Diagram
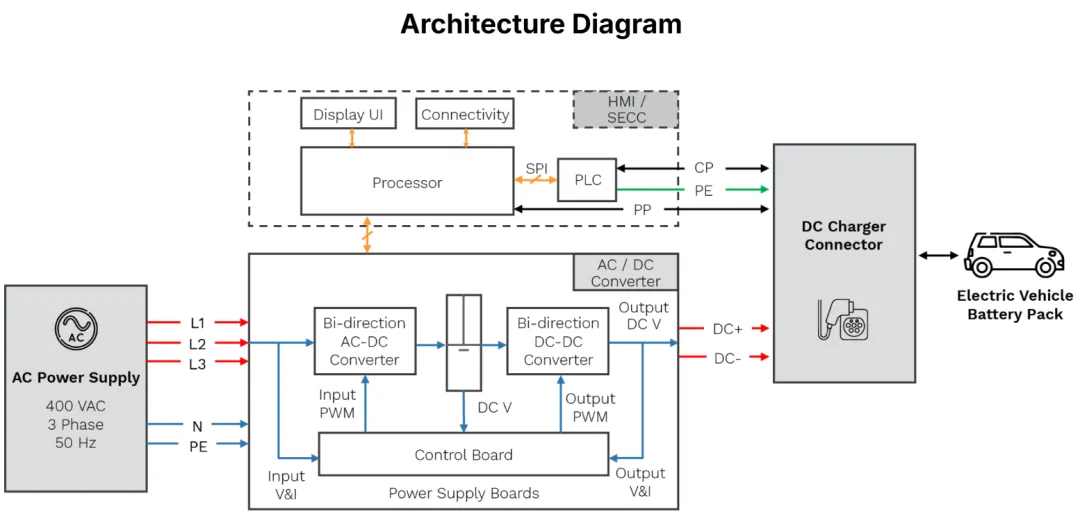
2. Charging control method of the charging system
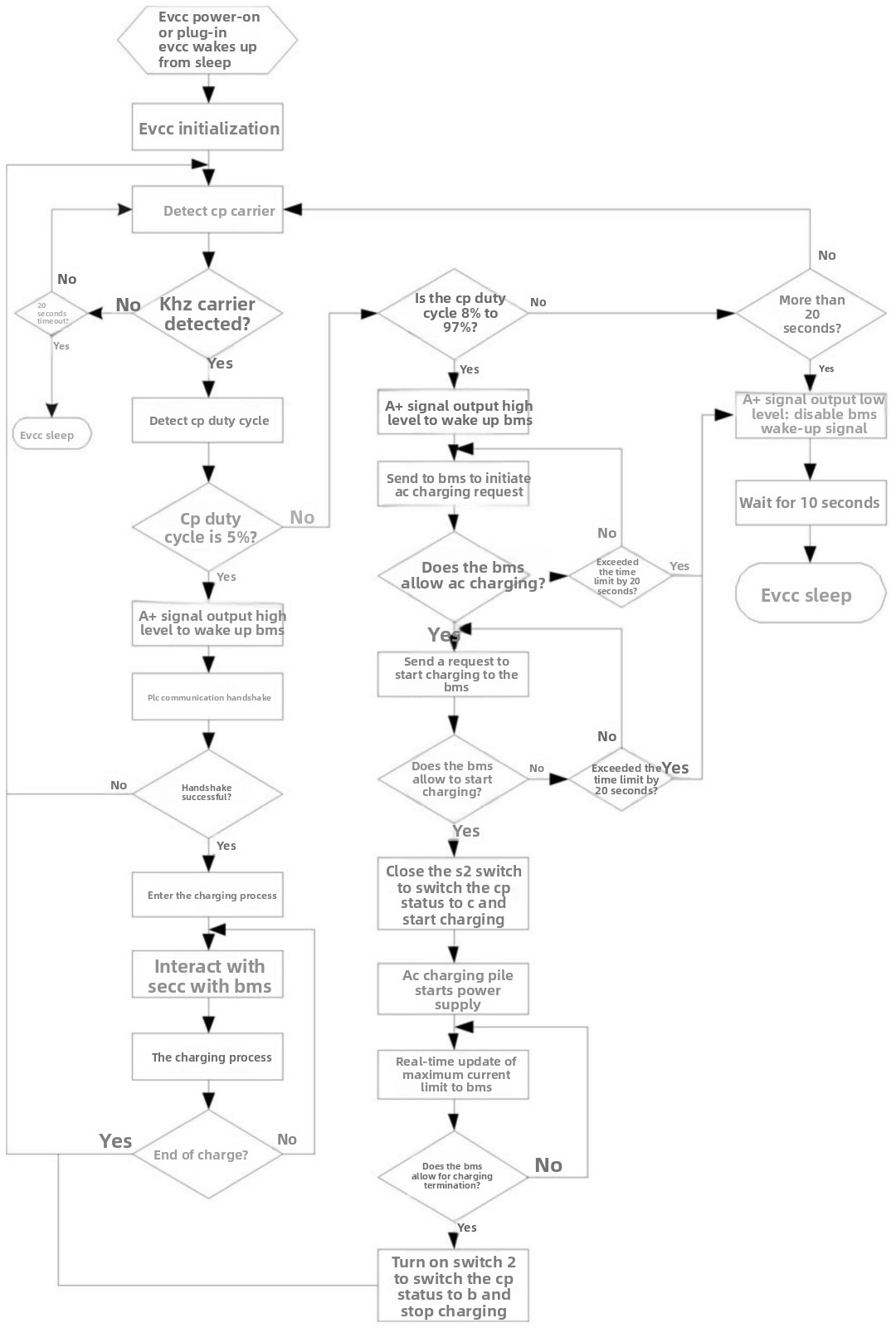
1) Manually power on the 12V DC power supply to put the EVCC into power-on state, or wake up the EVCC when theev charging gunis inserted into theelectric car charging dock. The EVCC will then initialize.
2) After the EVCC initialization is complete, it begins to detect the CP carrier of the charging dock.
3) If the CP carrier frequency is not 1kHz, the CP carrier frequency continues to be detected. If the CP carrier frequency is still not 1kHz after 20 seconds of detection, the EVCC enters sleep mode.
4) If the CP carrier frequency is 1kHz, the duty cycle of the CP signal terminal of the charging dock is detected.
5) When the duty cycle of the CP signal terminal is 5%, the EVCC outputs an A+ high-level signal to the BMS to wake up the BMS. Then, the EVCC and the SECC of the charging pile perform a PLC communication handshake. If the handshake fails, it returns to step 2). If the handshake succeeds, it enters the charging process.
6) When the CP duty cycle is 8%-97%, the EVCC outputs an A+ high-level signal to the BMS to wake it up. Then, the EVCC sends an AC charging request to the BMS.
7) If the BMS allows AC charging, it sends an AC charging confirmation to the EVCC, initiating the AC charging process.
8) If the BMS does not allow AC charging, it calculates whether the time taken to send the AC charging request to the BMS exceeds 20 seconds. If it does not exceed 20 seconds, it resends the AC charging request to the BMS. If it exceeds 20 seconds, the AC charging process ends.
9) When the CP duty cycle is neither 5% nor 8%-97%, it calculates whether the time taken to detect the CP duty cycle exceeds 20 seconds. If it does not exceed 20 seconds, it returns to the CP carrier detection step for processing. If it exceeds 20 seconds, the charging process ends.
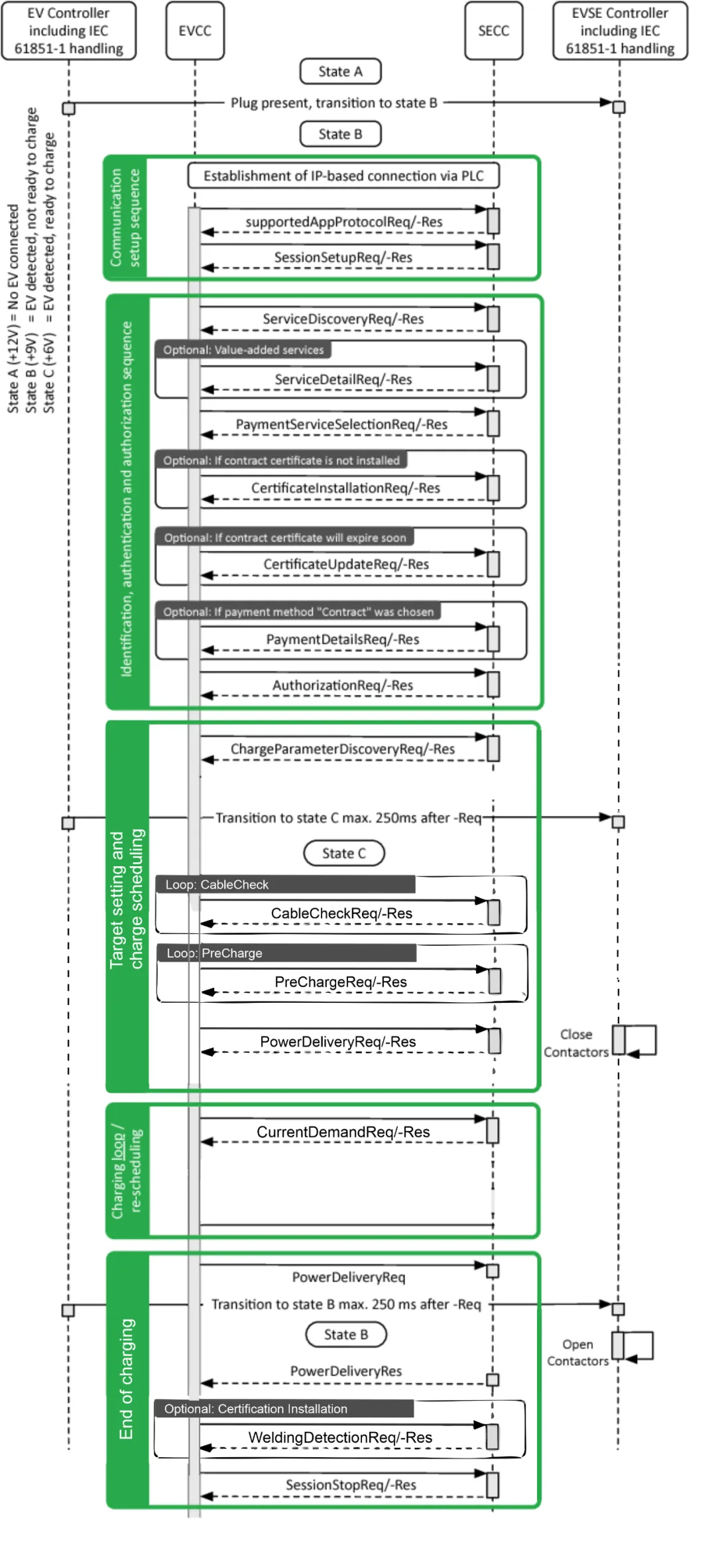
The PLC communication handshake process in step 5 includes the SLAC process, the SDP process, and the establishment of a TCP connection.
The charging process is as follows:
a. The EVCC and SECC begin V2G message exchange. Then, the SECC, based on the EVCC’s request message during the supported App Protocol handshake phase and theev charging station’sstatus, determines whether to use the DIN70121 or ISO15118 charging protocol. Additionally, during the supported App Protocol handshake phase, the EVCC sends the priority of its supported protocols to the SECC. Since different SECCs within differentelectric vehicle charging stationssupport different charging protocols (some support both DIN70121 and ISO15118, while others support only one), when the SECC supports both, it will select the protocol with the higher priority supported by the EVCC. When the SECC supports only one protocol, it can only select the corresponding protocol during the charging process.
b. When the SECC selects the DIN70121 protocol, theelectric car charging stationand theelectric vehiclewill begin DC charging.
c. When the SECC selects ISO 1511… 5.1.1.8 Protocol, and when theV2Gmessage exchange between EVCC and SECC reaches the ServiceDiscovery phase, SECC will inform EVCC of its payment method, energy transfer method, service ID, and service type;
d. Subsequently, when the V2G message exchange between EVCC and SECC reaches the PaymentServiceSelection phase, and EVCC selects External Payment as the payment method, EVCC and SECC will enter the EIM external authentication mode; if EVCC selects Contract Payment as the payment method, EVCC and SECC will enter the PNC plug-and-charge authentication mode;
e. When EVCC and SECC enter the external authentication mode and they interact to the ChargeParameterDiscovery phase, if the energy transfer method PEVRequestedEnergyTransfer requested by EVCC is AC, they will perform AC Charging EIM message set, i.e., EIM AC charging; if the energy transfer method PEVRequestedEnergyTransfer requested by EVCC is DC, they will perform DC… Charging EIM message set, i.e., EIM DC charging;
f. When EVCC and SECC enter the plug-and-charge authentication mode, and they interact to the ChargeParameterDiscovery stage, if the energy transfer method requested by EVCC (PEVRequestedEnergyTransfer) is AC, they will perform AC Charging PNC message set, i.e., PNC AC charging; if the energy transfer method requested by EVCC (PEVRequestedEnergyTransfer) is DC, they will perform DC Charging PNC message set, i.e., PNC DC charging.
The AC charging process in step 7 is as follows:
a. The EVCC cyclically sends AC charging current limit messages and charging start request messages to the BMS. If the BMS replies with a “start charging allowed” message, the EVCC and BMS enter the charging cycle phase.
b. During the charging cycle phase, the EVCC cyclically sends AC charging current limit messages and charging stop request messages to the BMS.
c. When the battery is fully charged or the charging stop condition is met, the BMS sends a charging stop message to the EVCC, and the EVCC enters the power-off process to end charging.
3. CCS Communication Flowchart
4. Program Flowchart
Post time: Dec-12-2025




