- “5 minutes of charging, 300 km of range” has become a reality in the field of electric vehicles.
“5 minutes of charging, 2 hours of calling”, an impressive advertising slogan in the mobile phone industry, has now “rolled” into the field ofnew energy electric vehicle charging. “Charging for 5 minutes, 300 kilometers of range” has now become a reality, and the problem of “slow charging” of new energy vehicles seems to have been answered. As a new technology to solve the “charging difficulty” of new energy vehicles, liquid-cooled supercharging technology has become the focus of industry competition. Today’s article will take you to understand the technology ofliquid cooling and superchargingand analyze its market status and future trends, hoping to give some inspiration and help to those who are interested.
01. What is “liquid cooling and supercharging”?
Working principle:
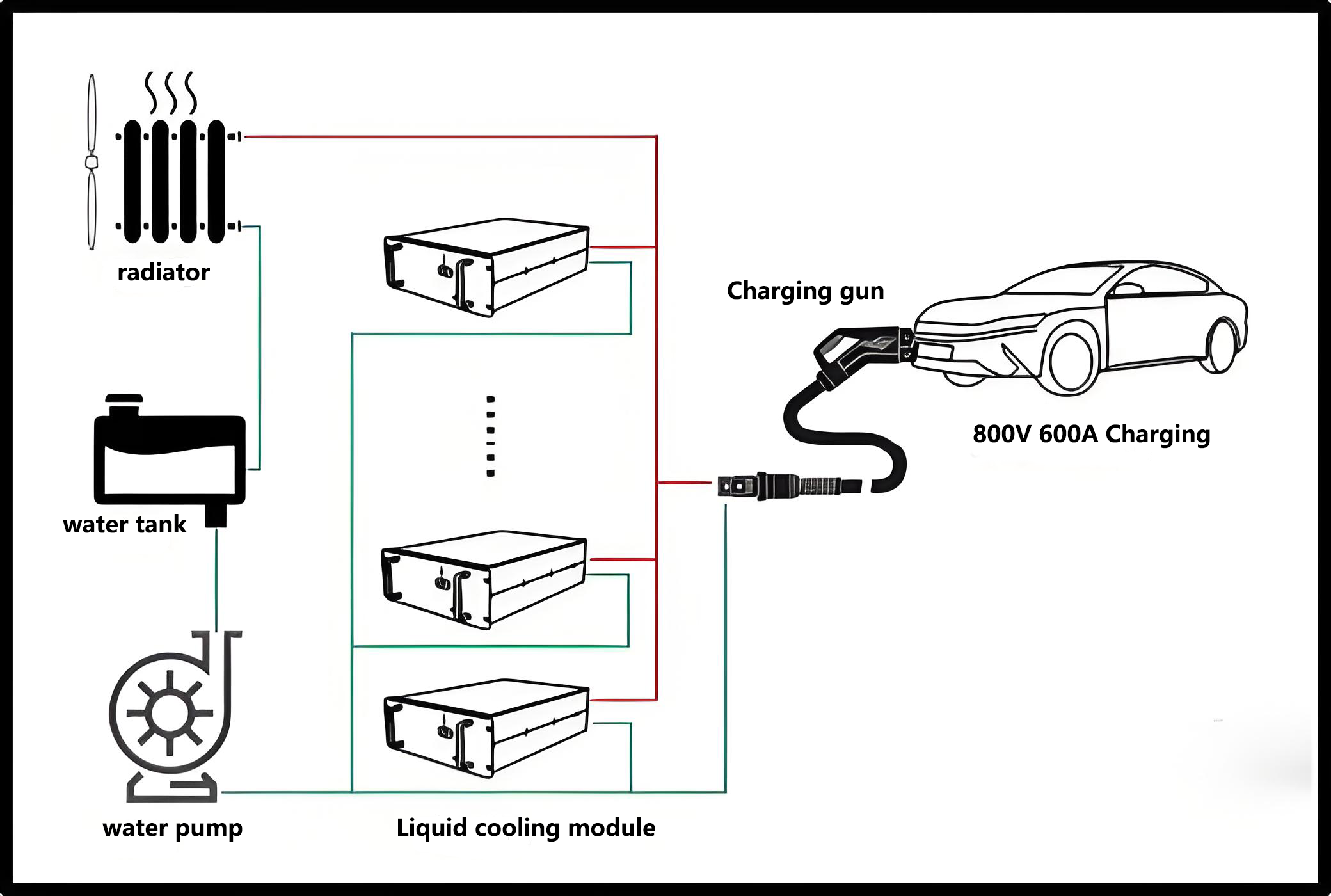
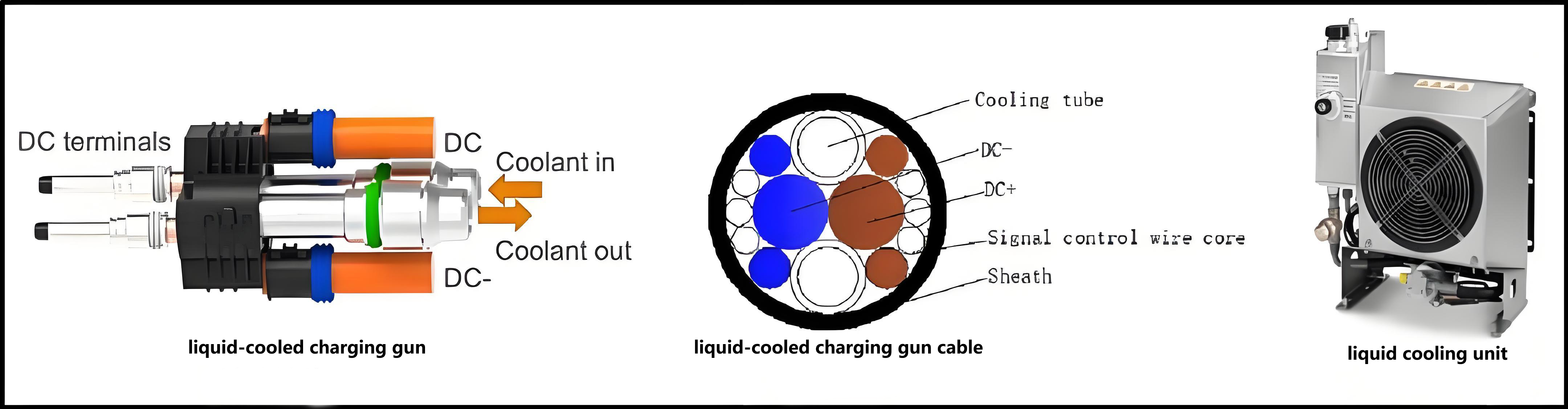
Liquid-cooled overcharging is to set up a special liquid circulation channel between the cable and theev charging gun, add liquid coolant for heat dissipation in the channel, and promote the coolant circulation through the power pump, so as to bring out the heat generated during the charging process.
The power part of the system adopts liquid cooling and heat dissipation, and there is no air exchange with the external environment, so it can achieve IP65 design, and the system adopts a large air volume fan for heat dissipation, low noise, and high environmental friendliness.
02. What are the advantages of liquid cooling and overcharging?
Advantages of liquid-cooled supercharging:
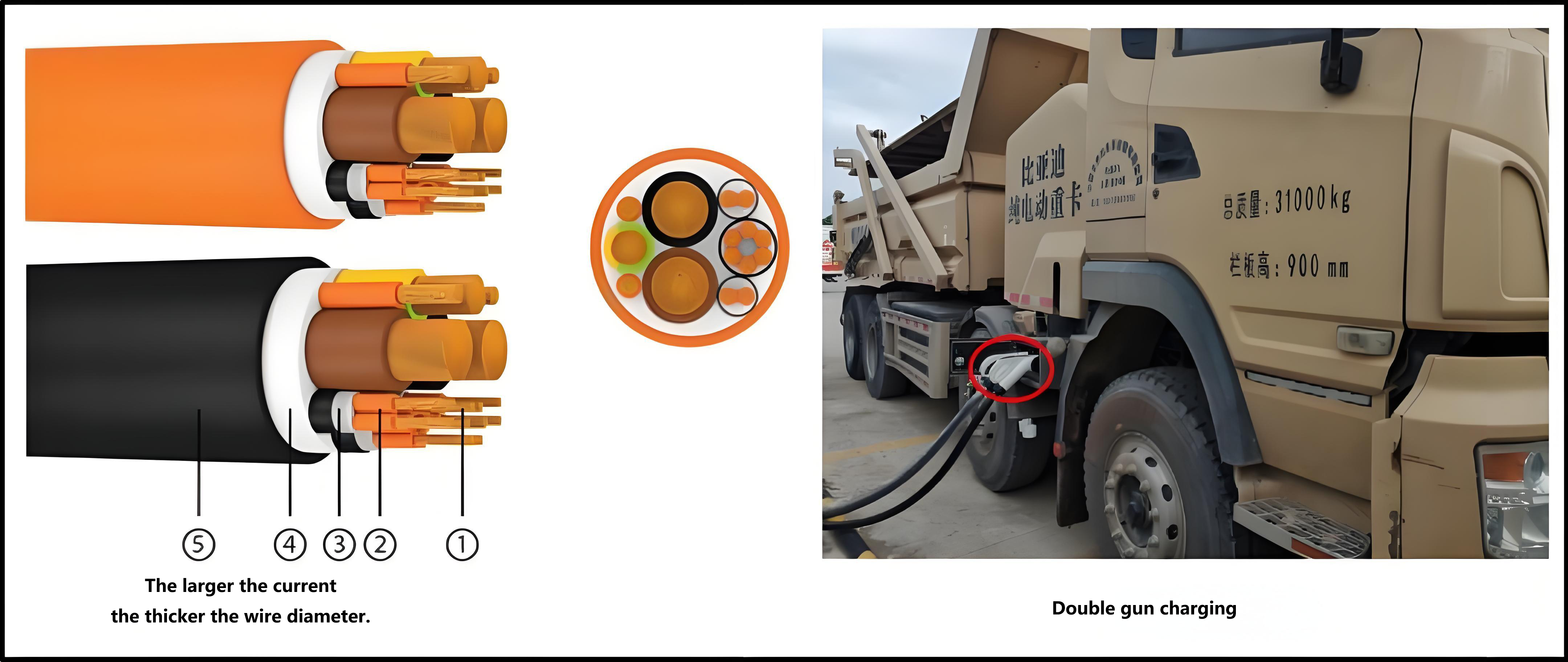
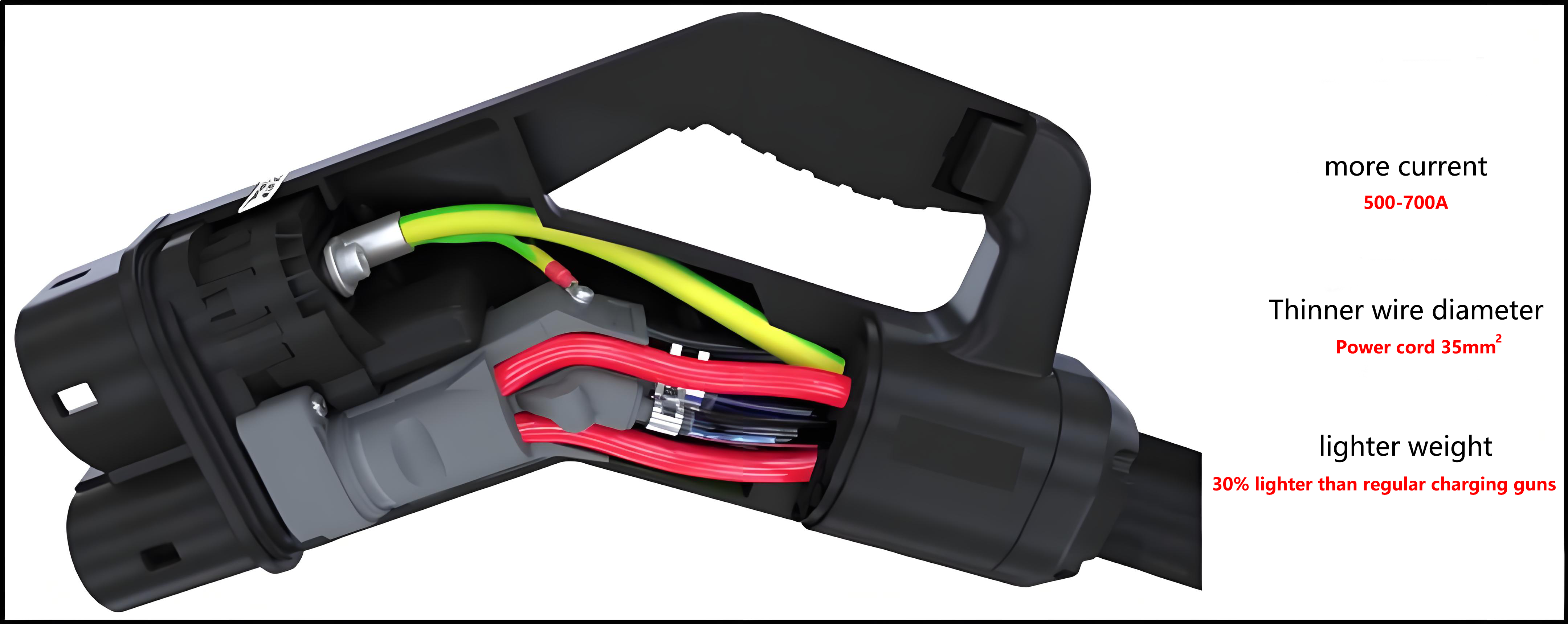
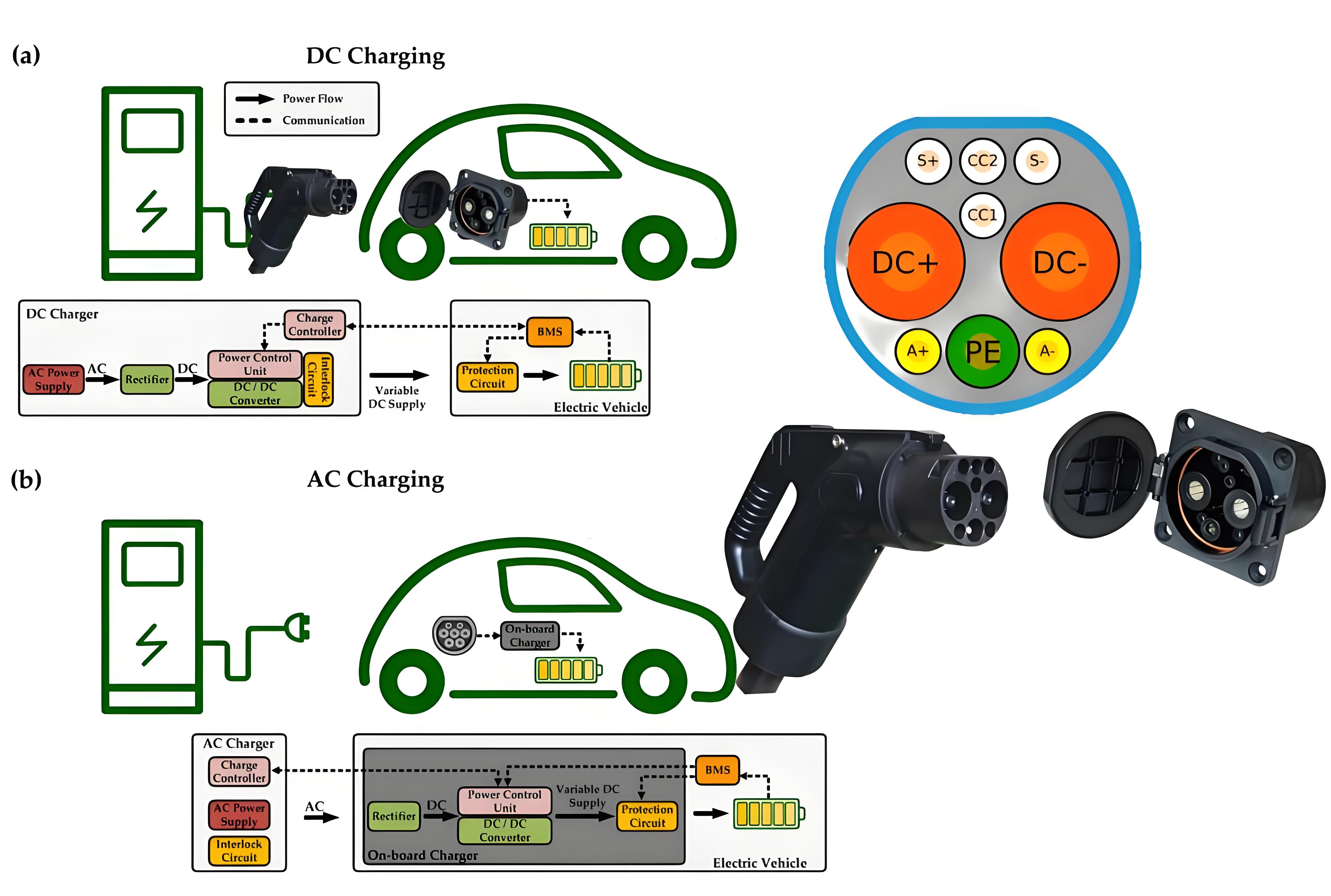
1. Larger current and fast charging speed.The output current of theev charging pileis limited by the charging gun wire, the copper cable in theev charger gunwire to conduct electricity, and the heat of the cable is directly proportional to the square value of the current, the larger the charging current, the greater the heating of the cable, to reduce the heat generation of the cable to avoid overheating, it is necessary to increase the cross-sectional area of the wire, of course, the heavier the gun wire. The current250A national standard charging gun(GB/T)generally uses an 80mm2 cable, and the charging gun is very heavy as a whole and is not easy to bend. If you want to achieve higher current charging, you can also usedual gun charging, but this is only a stopgap measure for specific occasions, and the final solution to high-current charging can only be liquid-cooled charging gun charging.
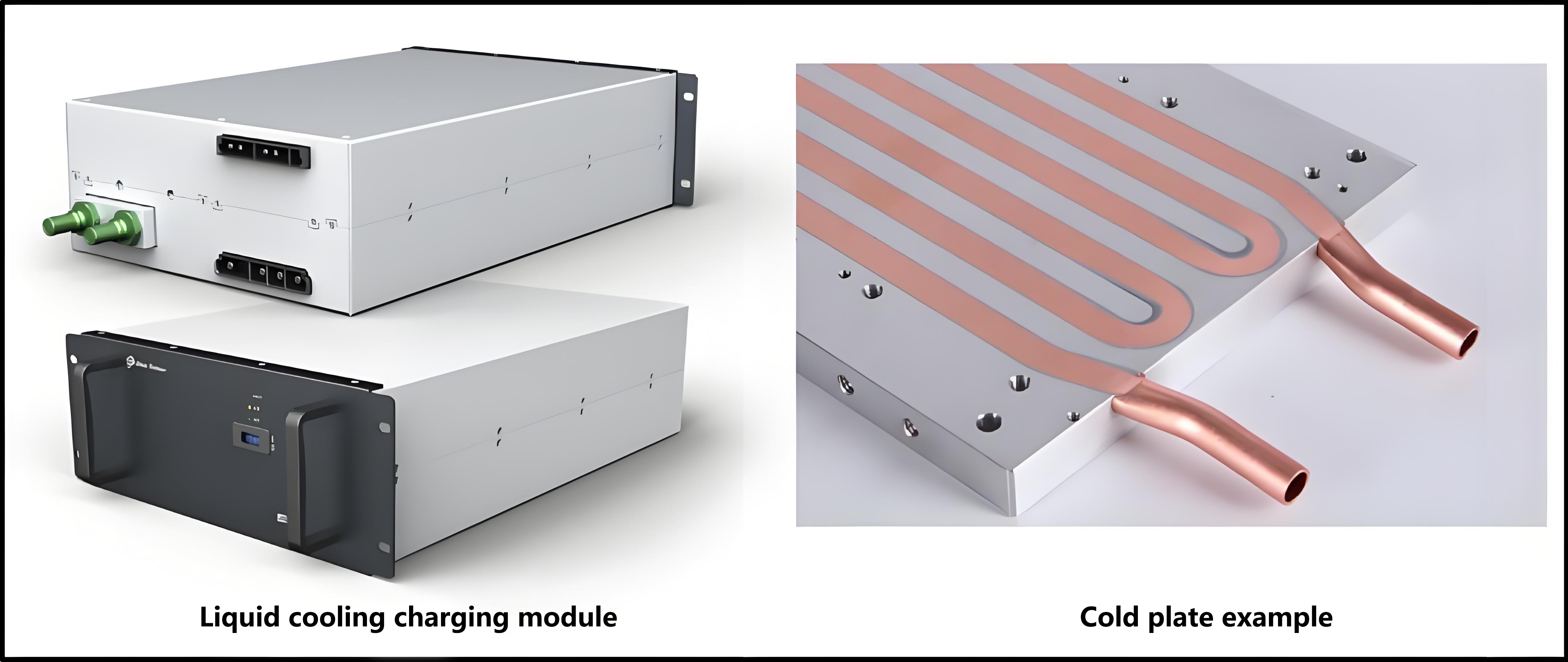
The cable of the 500A liquid-cooled ev charging gun is usually only 35mm2, and the coolant flow in the water pipe takes away the heat. Because the cable is thin, theliquid-cooled charging gunis 30%~40% lighter than the conventionalev charging gun. The liquid-cooledelectric car charging gunalso needs to be equipped with a cooling unit, which consists of a water tank, a water pump, a radiator and a fan. The pump drives the coolant to circulate through the gun line, bringing heat to the radiator and then blowing away by the fan, resulting in a larger ampampage than a conventionalnaturally cooled charging station.
2. The gun line is lighter, and the charging equipment is lighter.
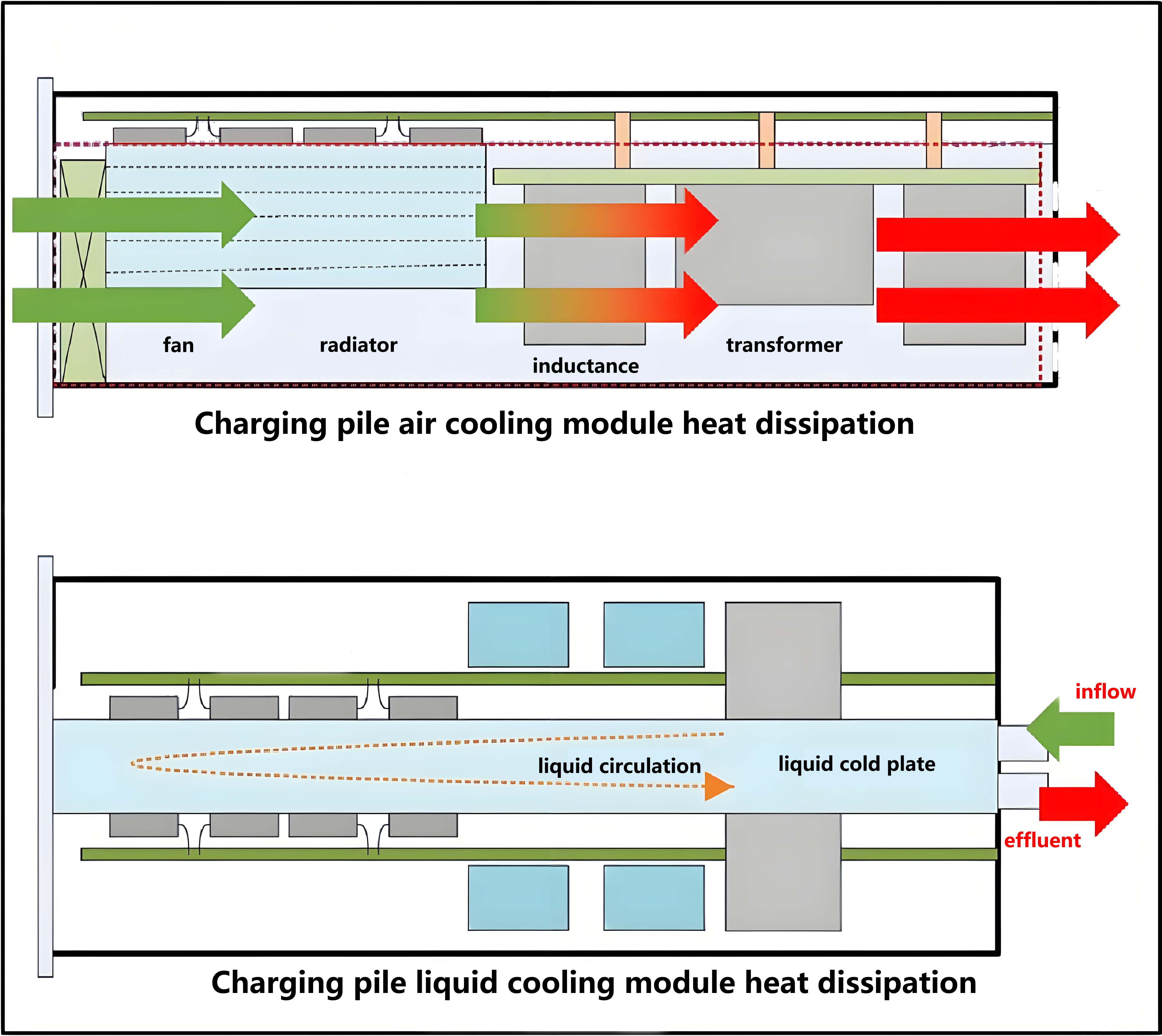
3. Less heat, fast heat dissipation, and high safety. Theelectric car charging stationbody of conventional charging piles and semi-liquid-cooledev charging stationsis air-cooled and heat dissipation, and the air enters the pile from one side, blowing away the heat of the electrical components and rectifier modules, and dissipating from the pile on the other side. The air will be mixed with dust, salt spray and water vapor and adsorbed on the surface of the internal device, resulting in poor system insulation, poor heat dissipation, low charging efficiency, and reduced equipment life. For conventionalelectric vehicle charging stationsor semi-liquid-cooledev car charging piles, heat dissipation and protection are two contradictory concepts.
The fullyliquid-cooled ev chargeradopts a liquid-cooled charging module, the front and back of the liquid-cooled module do not have any air ducts, and the module relies on the coolant circulating inside the liquid cold plate to exchange heat with the outside world, so that the power part of theelectric car chargercan be fully enclosed, the radiator is placed externally, and the heat is brought to the radiator through the coolant inside, and the external air blows away the heat on the radiator surface. The liquid-cooled charging module and electrical accessories in theelectric vehicle charging pilebody have no contact with the external environment, so that IP65 protection can be achieved and the reliability is higher.
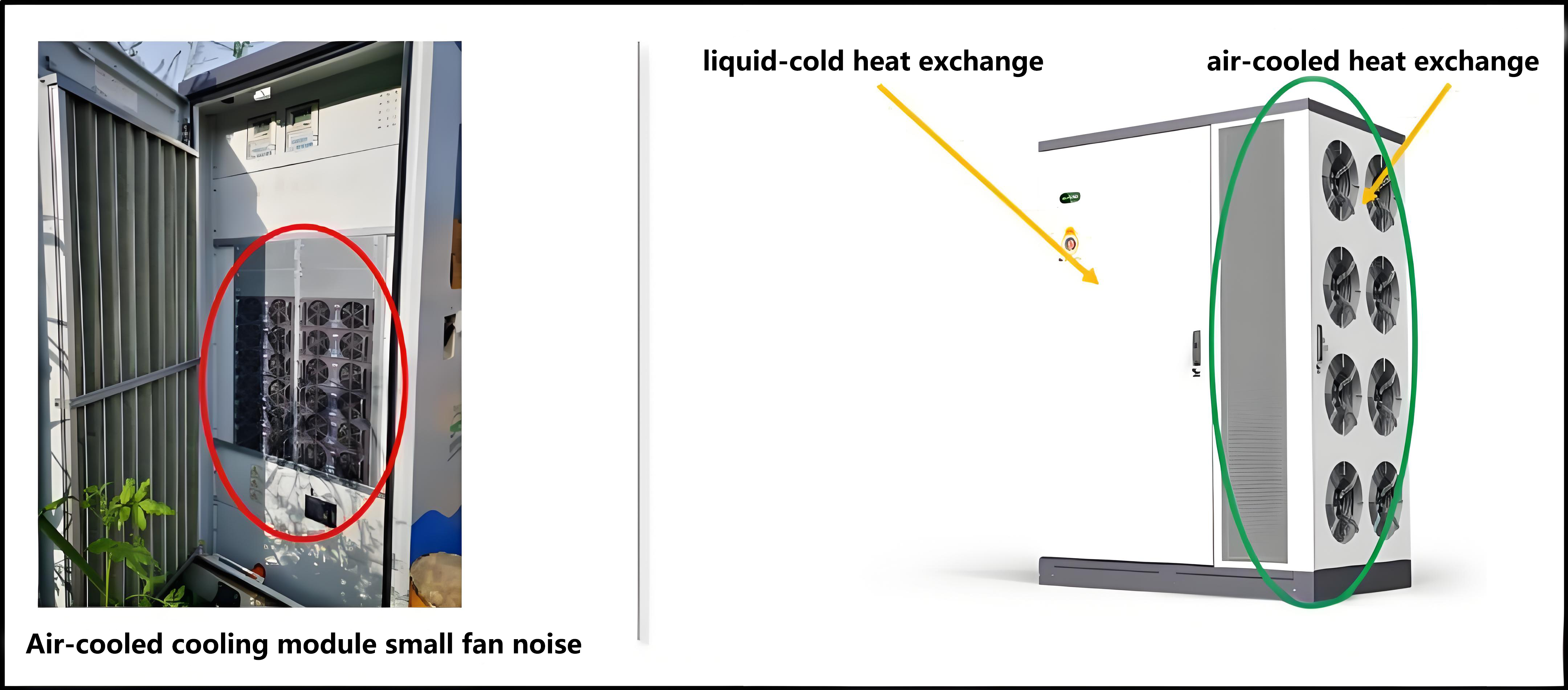
4. Low charging noise and higher protection level.Conventionalev charger stationsand semi-liquid-cooledelectric car chargershave built-in air-cooled charging modules, air-cooled modules have built-in multiple high-speed small fans, the operating noise reaches more than 65db, and there are cooling fans on theelectric car chargerbody. Therefore, the noise of charging stations is the most complained about problem by operators, and they have to be rectified, but the cost of rectification is high, and the effect is very limited, and in the end they have to reduce power and noise reduction.
The internal liquid-cooled module relies on the water pump to drive the coolant to circulate and dissipate heat, transferring the heat of the module to the fin radiator, and the external relies on a low-speed and large-volume fan or air conditioner to dissipate the heat on the radiator. The fully liquid-cooled supercharging pile can also adopt a split cooling design, similar to the split air conditioner, placing the heat dissipation unit far away from the crowd, and even exchanging heat with pools and fountains to achieve better heat dissipation and lower noise.
5. Low TCO. The cost ofcharging equipmentat charging stations must be considered from the full life cycle cost (TCO) of charging piles, and the traditional life ofcharging piles using air-cooled charging modulesgenerally does not exceed 5 years, but the current lease period forcharging station operationis 8-10 years, which means that at least one charging equipment needs to be replaced during the operation cycle of the station. On the other hand, the service life of the fully liquid-cooled charging pile is at least 10 years, which can cover the entire life cycle of the station. At the same time, compared with charging piles using air-cooledcharging modulesthat require frequent cabinet opening and dust removal, maintenance and other operations,fully liquid-cooled charging pilesonly need to be flushed after the external radiator accumulates dust, and maintenance is simple.
The TCO of the fullyliquid-cooled charging systemis lower than that of the traditional charging system using air-cooled charging modules, and with the widespread batch application of the fully liquid-cooled system, its cost-effective advantages will be more obvious.
Do you think that liquid-cooled overcharging of charging piles will become the mainstream charging trend?
Post time: Aug-04-2025